Thyroid Cancer – Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Of the many types of cancer that affect the human body, cancer of the thyroid gland is a relatively rare type. It typically involves the thyroid gland, which is a small, butterfly-shaped gland found in the front of the neck. It is characterized by swollen lymph nodes and changes in voice. It is essential to understand the causes of thyroid cancer, its symptoms, and the treatment options available for a better prognosis.
Causes of thyroid cancer
The exact cause of thyroid cancer has yet to be known, but certain factors have been determined as likely contributors. These factors are as follows:
- Exposure to high radiation levels from medical treatments or environmental sources can increase the likelihood of thyroid cancer.
- A meal plan low in iodine can contribute to thyroid cancer.
- Certain inherited genetic mutations can increase the possibility of developing thyroid cancer.
- If one has previously been diagnosed with certain cancers, such as breast, oesophageal, testicular, or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, then chances are high that one might be diagnosed with thyroid cancer as well.
- Thyroid cancer is also prevalent in women who are still menstruating.
Symptoms of thyroid cancer
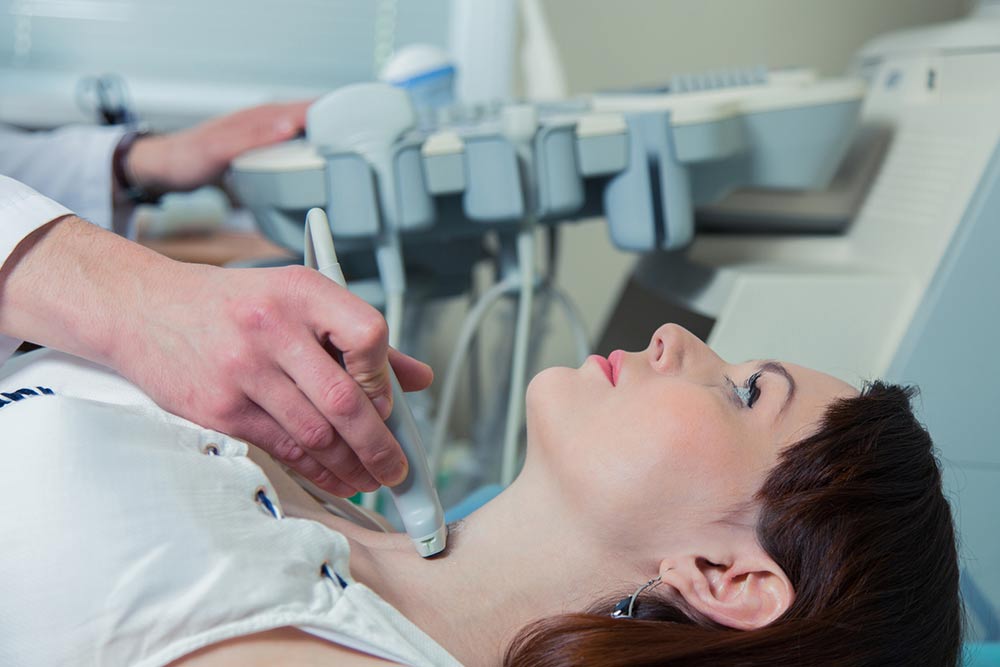
Thyroid cancer often gets diagnosed following a neck examination during a general physical checkup. Sometimes, X-rays conducted for some other reason can also detect thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer, in its early stages, often does not show any noticeable signs. However, as the disease advances, patients may experience symptoms such as the following:
- Lump or swelling in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Persistent cough unrelated to a cold or allergy
- Unexplained weight loss
However, other non-cancerous conditions can also give rise to similar symptoms. Therefore, if one experiences any persistent or concerning symptoms related to the throat or neck area, they should promptly consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and prompt diagnosis.
Managing thyroid cancer
Treatment options for thyroid cancer can depend on various factors. They include the stage and type of cancer and the individual characteristics of patients.
- The initial treatment approach involves surgery to remove the thyroid gland entirely by a process called thyroidectomy. Smaller tumors that have not spread outside the thyroid gland may be treated by removing a portion of the thyroid with the tumor through a process called a lobectomy.
- The main thyroid cancer treatment modalities include surgery (thyroidectomy), radioactive iodine therapy (RAI), external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and hormone replacement therapy.
- Well-differentiated tumors, such as papillary thyroid cancer and follicular thyroid cancer, can be treated and are usually curable. However, poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumors, such as anaplastic thyroid cancer, which are rare, can rapidly spread, lowering the chances of recovery.
- Most types of thyroid cancer can be fully cured in stages I and II, defined as the early stages. However, stage IV thyroid cancer is difficult to treat, with the prognosis being negative. If the cancer has spread to the brain, palliative care is given.
Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms of thyroid cancer is crucial for detecting the disease and treating it successfully. If concerns arise about one’s health condition or one suspects something is wrong with the thyroid gland, seeking medical advice immediately from a qualified healthcare provider is recommended.